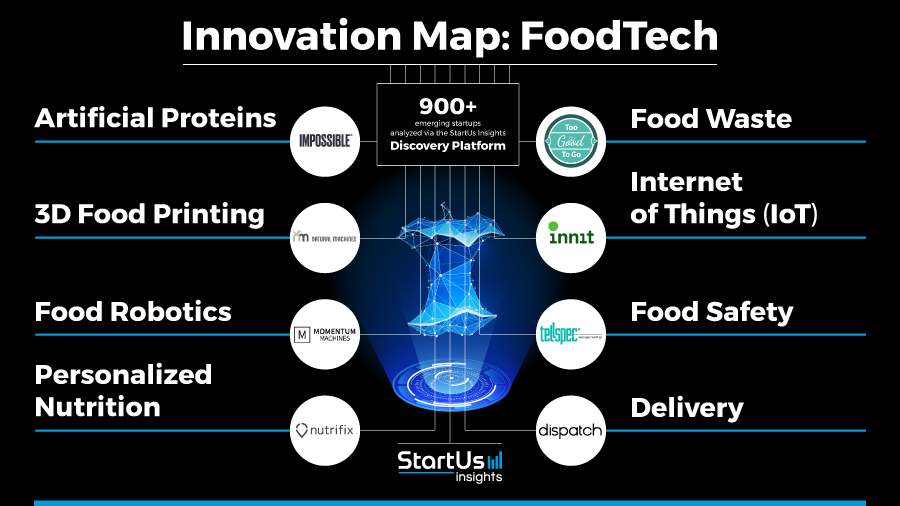
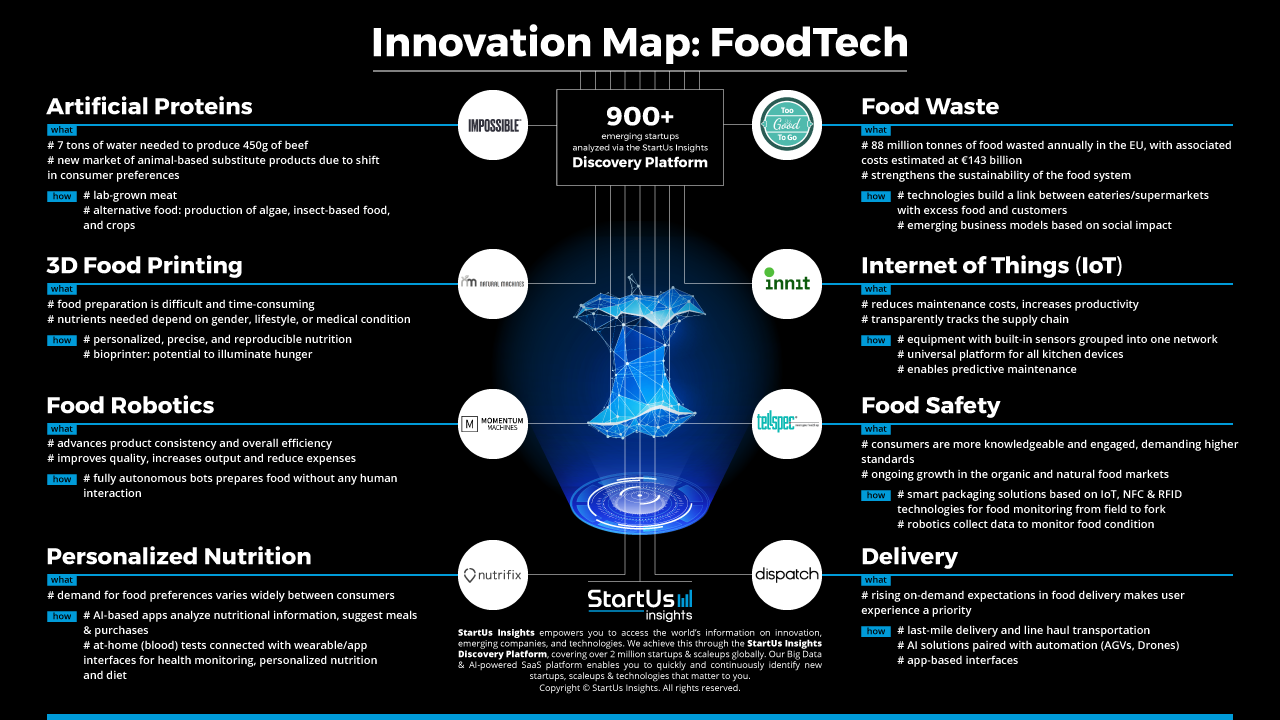
The rising demand for nutritious ingredients, product transparency, and environmentally-conscious sourcing have a powerful impact on companies in the food industry. As many are left uncertain by the various investment and innovation options that arise with these demands, we at StartUs Insights took a look at 900+ startups in the industry to identify key innovation areas and emerging technologies.
The findings presented in the Food Innovation Map cover eight areas which we identified using our proprietary AI- and data-driven innovation scouting approach. Let’s go through the results of our Food Innovation Map:
Artificial Proteins
Not considered affordable in 2013, the price for the production of roughly 140 grams of artificial meat has dropped from 274.366 Euro to 9,59 Euro in 2017. As the global demand for protein increases, lab-grown meat turns out to be the bright alternative. However, innovation does not stop with meat. Companies specialize in the production of algae, insect-based food, and crops consequently opening a new market of animal-based substitute products which will soon become the “new normal” as consumers progressively choose food options that meet their moral principles.
3D Food Printing
By using various types of powdered or liquid food material, 3D food printers bring extra nutritional value to our plates and additional revenue to food companies. Food printers take us one step closer to the era of personalized, precise, and reproducible nutrition as they allow to print the correct percentage of nutrients required for a particular gender, lifestyle, or medical condition. A specialized form of a 3D food printer is the bioprinter, currently in an experimental phase. This variant prints living cells (not exclusively used to produce food) and has the potential to illuminate hunger in areas of the world that need access to fresh foods.
Food Robotics
With an estimated worth of €2.1 billion by 2022, robotics improve quality, increase output and reduce expenses, especially in food and liquid processing. Food companies utilize robotics to advance product consistency and overall efficiency resulting in better tasting and healthier food for the consumer while businesses can apply resources in high-quality and sustainable ingredients.
Personalized Nutrition
The need and demand for therapeutic and lifestyle diets, nutritional value, as well as food preferences vary widely among consumers which is why personalized meals have already made their mark in the industry. However, adding software and hardware solutions such as 3D augmented/virtual reality applications with elements of image recognition or sensor technologies that measure chemicals, gluten etc. into this mix adds a clever twist as they allow to analyze nutritional information, suggests meals, and give advice on what foodstuff to purchase or order. Moreover, at-home (blood) tests connected with wearables and app interfaces enable health monitoring as well as truly personalized nutrition.
Food Waste
A staggering 88 million tonnes of food is wasted annually in the EU alone, with associated costs estimated at €143 billion. Selling food at a lower price or giving it to people in need are ideas already in place, however, they do become increasingly more relevant. As every stakeholder, from farmers to vendors and ultimately consumers, plays a role in strengthening the sustainability of the food system, social impact companies and startups generate viable business models to solve this problem.
Internet of Things (IoT)
Reduced maintenance costs, higher productivity, the transparent tracking of the supply chain as well as predictive maintenance are only a few of the advantages that the Internet of Things offers to the food industry. One example of an application is the smart kitchen, approaching reality at a fast pace. In a smart kitchen, devices and equipment with built-in sensors are grouped into one network of data that continuously exchanges information.
Food Safety
Today’s consumers are more knowledgeable and engaged and demand higher standards due to multiple high-profile incidents (e.g. 2013’s horse meat scandal). Monitoring food from field to fork with smart packaging solutions based on the Internet of Things, NFC & RFID technologies empower consumers as well as producers to monitor food conditions (e.g. freshness, ripeness, etc.) thus addressing this rising challenge.
While robotics also support this process by employing automated sensors and other hardware that regularly collects and sends data regarding the food condition, automation also improves every stage of the food manufacturing process. Through the integration of robotics, some tasks can be automated thus replacing the human workforce and eliminating the risk of human error.
Delivery
Industries such as logistics already benefit from innovations in the delivery process through application areas such as last-mile delivery and line-haul transportation. As food delivery accounts for the biggest share in the last-mile delivery market, it not only benefits from models based on shared mobility, courier and inner-city delivery (think Uber Eats, Foodora, etc.) but also promotes new models with focus on artificial intelligence (AI) solutions paired with automation strategies such as automated guided vehicles (AGVs).
Slow moving pavement droids that can travel up to 4 mph for roughly 10 miles to deliver food, and use a GPS signal as well as cameras to navigate and avoid obstacles are already being tested to streamline processes and harness data to make user experience (UX) a priority.
Disruptive Startups In The Food Industry Include:
- Impossible Foods creates the plant-based Impossible Burger, described by some as “the game changer in the food industry”. Made with soy leghemoglobin, a protein that carries heme, it mimics the taste of actual meat.
- Natural Machines develops the 3D food printer Foodini and promotes cooking with fresh ingredients. The printer uses open capsules that users load up with foodstuffs of their choice to create savory or sweet cuisine.
- Momentum Machines develops a fully autonomous burger-bot that can slice toppings, grill a patty, assemble and bag a burger without any human interaction. The burgers are fresh-ground, grilled to order and accented by a custom variety of produce, seasonings, and sauces.
- London startup Nutrifix recommends meals to cook, buy, or have delivered, tailored to consumers’ nutritional needs. Their app takes age, height, weight and health goals into consideration to calculate a personal recommended daily allowance and guides users toward their body’s needs.
- UK-based anti-food waste startup Too Good To Go acts as a link between eateries with excess food and customers who can place orders via an app to collect it at a discounted price.
- Innit introduces a universal platform for all kitchen devices capable of analyzing the number of items in a refrigerator, monitoring their expiration-date, suggesting recipes and even preparing meals.
- TellSpec develops a comprehensive solution for cloud-based spectroscopy. The patented AI-based real-time cloud analysis engine helps monitor events of food fraud as well as of food contamination locally and in specific regions.
- Dispatch creates a platform for local delivery powered by a fleet of autonomous vehicles designed for sidewalks and pedestrian spaces. The startup plans on mitigating the cost of delivery due to savings in labor costs by bringing packages right to a customer’s door and making their service available to the masses.
New perspectives and emerging technologies are the driving forces behind the transformation of the food industry. Estimated to reach a staggering value of €7.2 billion by 2020, the global food retail market continues to thrive as new competitors enter the market.
The innovation areas we outline in this Food Innovation Map are but a few of the emerging technologies we identified during our research. Dehydrated and low-processed food, augmented transparency and biological techniques to decrease the number of greenhouse gases emitted from food production begin to extend their influence on the industry – companies that partner with emerging startups to innovate will experience a clear-cut competitive advantage.